
Road Tunnels Manual

Road Tunnels Manual
In terms of resistance to high temperatures, tunnel equipment and cables can be broadly grouped as either fire-rated or unprotected.
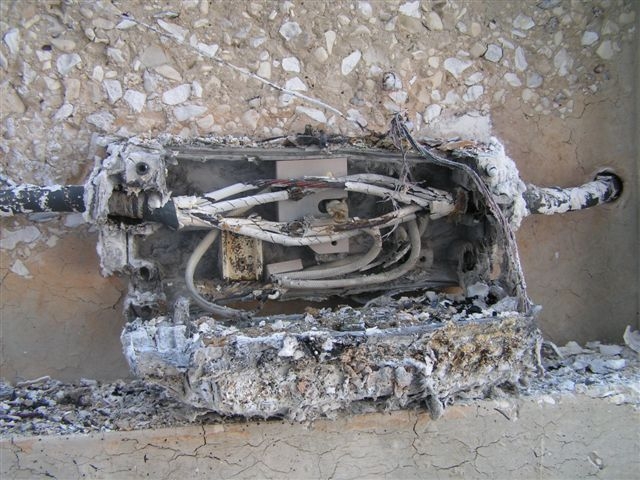

Protected equipment and cables with variable levels of resistance to fire include, for example:
Unprotected items of equipment such as traffic signs, cameras and public address (PA) speakers have working temperatures typically up to 50°C, and are likely to fail at relatively low temperatures. Materials include:
 Critical temperatures for materials used in such unprotected items include:
Critical temperatures for materials used in such unprotected items include:
All fittings used for the fixing of equipment to the structures should be considered in terms of their behaviour in fires.